1. What’s Funding Rate Arbitrage?
In order to anchor futures prices with spot prices, crypto perpetual futures markets introduce the funding rate mechanism. According to the mechanism, if the market turns bullish and bulls dominate the market, perpetual futures prices will be higher than spot prices, with the funding rate being positive, which means the long side needs to pay the funding fees to the short side. It will be the opposite when the funding rate is negative. Please see below for detailed rules:
When the funding rate is positive, long position holders (contract buyers) needs to pay funding fees to short position holders (contract sellers); when the funding rate is negative, short position holders (contract sellers) needs to pay funding fees to long position holders (contract buyers).
Please note: FUTX’s funding fees settlement occurs every 8 hours at 00:00 UTC, 08:00 UTC and 16:00 UTC.
Therefore, theoretically, regardless of price volatility risks, positions holding tokens with a constantly high level of funding rate may earn higher returns. In other words, if a token comes with a high funding rate that persists for a long time, investors can continue benefiting from holding the token by leveraging the funding rate mechanism.
Take OMI perpetual futures contracts as an example, the funding rate on OMI perpetual futures contracts remains positive in a high level for a long time as per the funding rate history of perpetual futures contracts on FUTX, which means users are able to earn from funding fees by just holding a short position of OMI.
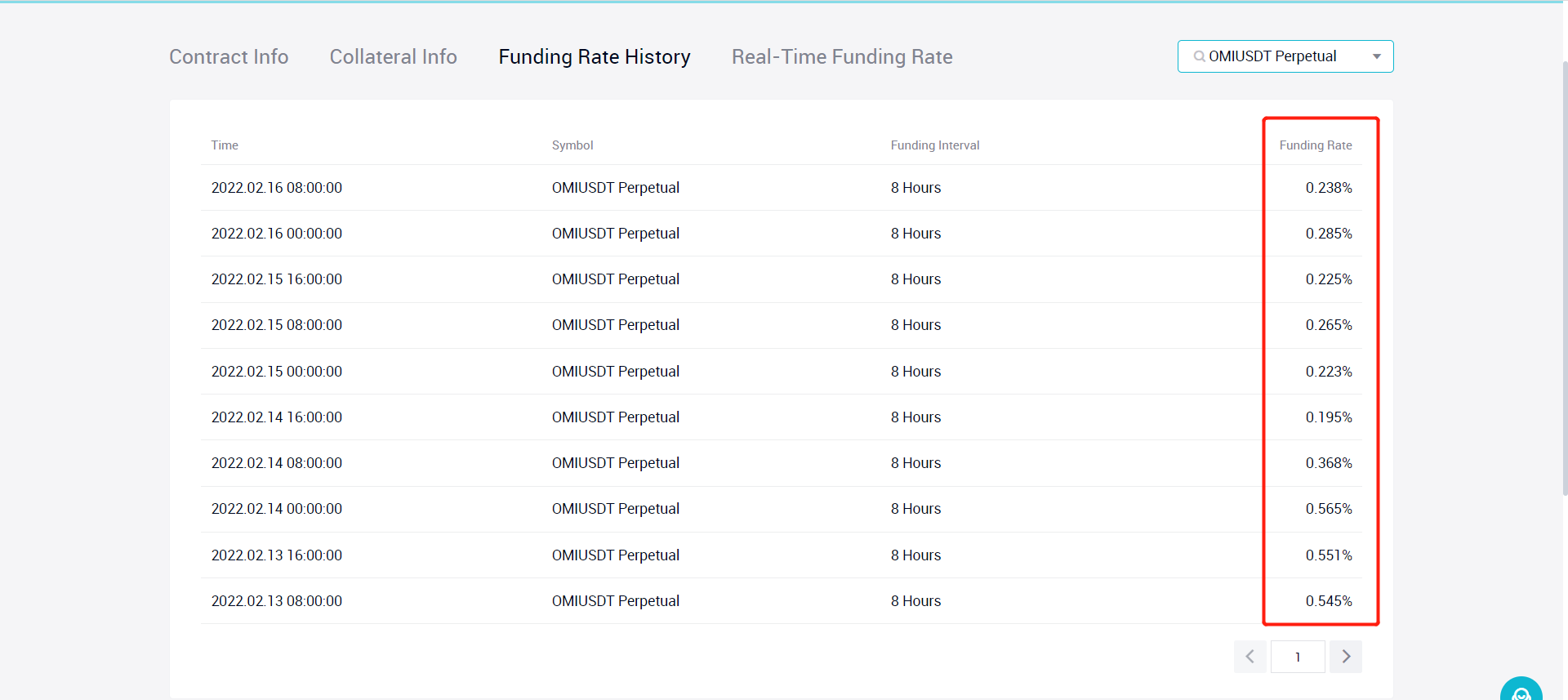
But it's important to note that the above profit strategy does not take account of price volatility risks. In theory, although investors can benefit from funding fees by just holding a short position of OMI, they will suffer a loss from the position holding once the market trend runs against early expectations, i.e., the OMI price rallies. To hedge the risk, investors need to buy the equivalent of OMI in the spot market or hold long positions of the asset with the same value in the margin market.
2. Core Strategy of Funding Rate Arbitrage
To master the funding rate arbitrage, there are two key aspects investors should factor in:
1) Select a token with a high funding rate that persists for a long time
To arbitrage from funding fees, investors should select the token with a high funding rate that lasts for a long time.
Please note: Before implementing the funding rate arbitrage, you can view the latest updates and history data regarding the funding rates of all futures tokens on FUTX for reference.
2) Hedge volatility risks by holding opposite positions in the spot/margin market
To reduce price volatility risks, users who adopt the funding rate arbitrage for perpetual futures trading need to hold opposite positions of the same value in the spot or margin market to hedge the trading risks, thus achieving long-term profits.
3. Steps to Arbitrage from Funding Fees
Simply put, users should hold a position in perpetual futures trading and an opposite position of the same value in spot/margin trading.
1) Arbitrage from funding fees - Perpetual futures/spot hedging
a. Buy spot assets
b. Open a short position of the assets with the same value in the perpetual futures market
c. Choose a time to close the position and sell the spot asset to earn a profit
Take OMI perpetual futures contracts as an example, assume the funding rate of OMI is 0.422% and is expected to rise to 0.566%. User A buys 10,000 USDT worth of OMI in spot trading while opening a short position of OMI with the same value in perpetual futures trading. In the next funding interval, the user is expected to earn 10,000 USDT*0.556%=55.6 USDT. Assume the funding rate will remain at this level for a week, which means the user will earn 55.6*3*7=1167.6 USDT from a one-week holding of the position. (Please note: To facilitate understanding, the case does not take into account position value changes arising from price actions during the holding period.)
Please note: Hedging can only be realized when the spot and futures positions are equal in value.
2) Arbitrage from funding fees - Perpetual futures/margin hedging
As margin trading involves interest rates, users need to consider the potential impacts of interest rates while adopting the funding rate arbitrage.
a. When the funding rate is positive and is greater than the sum of the interest rate and transaction fees, the short side will receive the funding fee from the long side, i.e., buying the asset in margin trading while opening a short position of the asset with the same value in perpetual futures trading.
b. When the funding rate is negative and is greater than the sum of the interest rate and transaction fees, the long side will receive the funding fee from the short side, i.e., selling the asset in margin trading while opening a long position of the asset with the same value in perpetual futures trading.
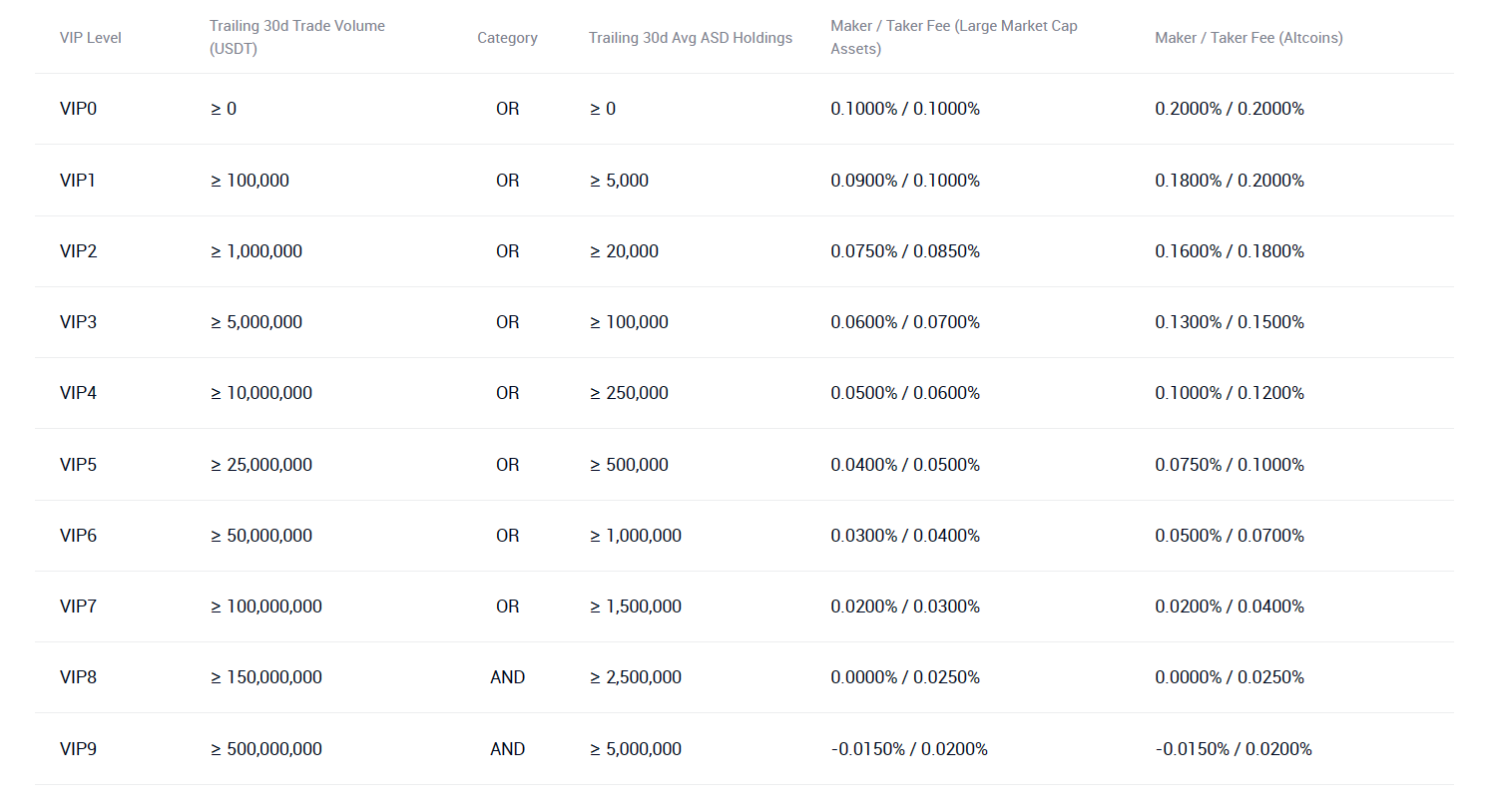
Overall, considering transaction costs, the difference between funding rates (floating rates) in perpetual futures trading and fixed fee rates is the key to how much you can arbitrage from perpetual futures and spot margin trading. Given the futures funding rate unchanged, in order to earn a large profit, users need to minimize fixed fee rates, namely reducing the interest rate and transaction fees. FUTX adopts a tiered fee rate system. The higher the account level, the lower the fee rates. Users can refer to FUXT’s fee rates system to develop an appropriate funding rate arbitrage accordingly to earn higher returns.
4. Notes on Funding Rate Arbitrage:
1) Lower leverage to avoid liquidation. As perpetual contracts prices move in tandem with spot price actions, there is lower risks or even no risks in funding rate arbitrage. However, users should be still aware of liquidation risks caused by large price fluctuations.
2) Do market research and be cautious about token selection. To arbitrage from funding fees, users need to make their own market research on the assets to buy and their funding rates so as to choose the right token with a higher funding rate that lasts for a long time.
3) Invest properly to reduce trading risks. Slippage may occur if massive investments are plunged into a small-cap token with a limited market depth.
4) Do not change investment assets and adjust positions frequently. Frequently adjusting positions and changing investment assets for hedging will make profits earned fail to cover transaction costs.
